Baseboard heating systems are a popular choice for home heating, and they are known for their efficiency and ability to distribute heat evenly. These systems rely on hot water circulating through pipes and baseboard radiators to warm a space. However, a common issue that can disrupt their performance is air becoming trapped in the system. This trapped air can reduce heating efficiency, create uneven heating across rooms, and even produce annoying gurgling or banging noises.

The purpose of this guide is to provide you with a clear, step-by-step explanation of how to remove air from baseboard heating systems. By following these instructions, you can restore the efficiency and comfort of your heating system.
Safety is paramount when working with hot water and pressurized systems. Always take appropriate precautions, such as allowing the system to cool and ensuring you have the right tools to prevent any accidents or injuries.
Understanding Why Air Gets Trapped in the System
Causes of Air Buildup
Air may become trapped in a baseboard heating system for several reasons. One common cause is the initial filling of the system or performing recent maintenance. When the system is first filled with water or undergoes repairs, air pockets can inadvertently enter the pipes. Additionally, small leaks in valves or connections may introduce air over time, even if the leaks are minor and go unnoticed. Finally, normal operation of the heating system can lead to gradual air accumulation over an extended period, as air naturally dissolves into and separates from water under certain conditions.
Signs of Air in the System
Recognizing the signs of trapped air in your baseboard heating system is essential for proper maintenance. One of the most noticeable indicators is gurgling or bubbling noises when operating the system. These sounds suggest air is circulating with the water, disrupting the flow. Another common symptom is the formation of cold spots on baseboard heaters, where radiator sections fail to heat properly. Lastly, a significant reduction in the overall heating efficiency may indicate that air impedes the system’s performance, leaving rooms less comfortable despite the active heater.
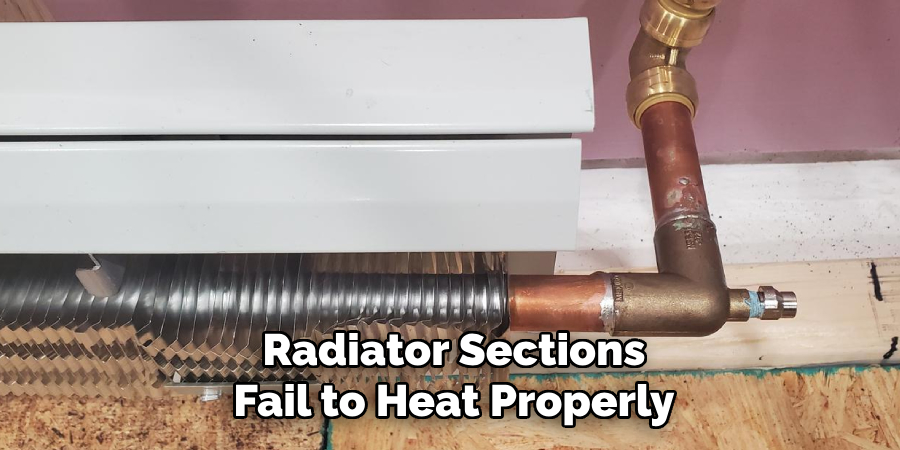
Tools and Safety Precautions
Essential Tools
- Flathead screwdriver or radiator key (depending on your model): Used to loosen the bleed valve on baseboard heaters.
- Bucket or towels: It is necessary to catch any excess water that may escape during the process of bleeding.
- Gloves and safety goggles: Provide hand protection from hot elements and shield your eyes from potential splashes of hot water.
Safety Precautions
Before attempting to bleed air from your baseboard heating system, ensure that the heating system is fully turned off. This prevents accidental hot water circulation, reducing the risk of burns or injuries. Additionally, allow a few minutes for the system to cool down if it has recently been used. When opening the bleed valve, proceed slowly and carefully to relieve pressure gradually, as hot water may escape initially. Wearing gloves and goggles adds extra protection, ensuring your safety. Always have a towel or bucket nearby to manage any leaks or spills and prevent water damage to surrounding areas. Prioritizing safety and using the appropriate tools will help make the process smooth and hazard-free.
Locating the Air Bleed Valves
Step 1: Identify the Type of Baseboard Heating System
Before locating the air bleed valves, it is crucial to determine the type of baseboard heating system you have. Generally, two standard setups are series loop systems and multi-zone systems. A series loop system consists of a single loop where water travels through each baseboard unit sequentially. Bleed valves in this system are typically located on each baseboard unit. On the other hand, a multi-zone system includes multiple loops, each controlled separately for specific areas of your home. For multi-zone systems, bleed valves may be present on individual baseboard units or near the basement or utility room boiler.
Step 2: Find the Highest Bleed Valve
Since air naturally rises to the highest point in a water-based heating system, it is best to start bleeding air from the upper floors of your home, if applicable. Inspect the baseboard units on the highest floor to locate manual bleed valves. These valves are often small and easily overlooked, so take your time to identify them correctly.

If your system lacks manual bleed valves on the baseboard units, the air may need to be released directly at the boiler. To manage this task, look for an auto-vent or manual air vent located near the boiler. Properly locating the bleed valves ensures you can perform the bleeding process efficiently and helps prevent recurring issues in the system.
How to Remove Air from Baseboard Heating System: Bleeding Air
Bleeding air from your baseboard heating system is essential to maintain its efficiency and ensure even heating throughout your home. Entrapped air can hinder water circulation, causing uneven temperatures or noisy operation. Follow these steps to bleed the system safely and effectively:
Step 1: Turn Off the System and Let It Cool
Before starting, shut off the thermostat to prevent water circulation. Allow the pipes and radiator units to cool down completely. This step ensures you can handle the valves and surrounding components safely without risk of burns or injury.
Step 2: Open the Air Bleed Valve
Locate the air bleed valve on your baseboard unit or near the boiler if necessary. Turn the valve slowly counterclockwise to open it using a screwdriver or a bleed valve key. You should hear a hissing noise as trapped air begins to escape from the system. Keep the valve open until the hissing sound diminishes, indicating most of the air has been released.
Step 3: Close the Valve When Water Flows Steadily
Once water starts flowing continuously through the open bleed valve without any air bubbles, close the valve clockwise. Ensure it is tightly sealed to prevent leaks. Repeat the process on all other home baseboard units requiring air bleeding. Performing this task for each affected unit will restore optimal system performance and eliminate cold spots.
Removing Air from the Boiler
If your heating system does not have individual bleed valves on the baseboard units, you must remove air directly from the boiler. Start by locating the air separator or auto-bleeder installed near the boiler. This component is designed to release trapped air automatically but may sometimes require manual assistance. If there is a system pressure release valve, open it slightly to help release excess air. Be sure to monitor the process and close the valve immediately once air is expelled.

Checking System Pressure
After bleeding air from the boiler, it is essential to check the system pressure to ensure proper functionality. Look at the pressure gauge on the boiler and confirm it is within the recommended range, typically between 12-20 PSI for most standard residential systems. If the pressure is too low, add water to the system slowly, making sure not to overfill. Verify the pressure again after adding water and adjust as necessary. Proper pressure maintenance ensures the heating system operates efficiently and prevents future issues related to trapped air or inadequate circulation.
Testing the System and Preventing Future Air Buildup
Once you have completed the previous steps, it is time to test the heating system to ensure it is functioning optimally. Start by turning the heating system back on and setting your thermostat to a comfortable level. Allow the system time to circulate heat, and then check each baseboard unit to confirm they are heating evenly. Uneven heating may indicate that air remains trapped within the system.
While the system is running, listen closely for any unusual gurgling or hissing sounds, as these noises could suggest that additional air needs to be removed. If you notice such sounds or experience uneven heating, repeat the air bleeding process described earlier. Ensure that you monitor the system pressure each time you conduct this process.

To prevent air buildup in the future, it is essential to perform routine maintenance. Regularly check the system for any signs of leaks, as these can allow air to enter the system. Additionally, ensure that the pressure remains within the recommended range and inspect both the expansion tank and automatic air vents at least once a year. These proactive measures will help maintain the efficiency of your heating system and minimize the risk of recurring air problems.
Conclusion
Understanding how to remove air from baseboard heating system is essential for maintaining optimal heating efficiency. Trapped air can disrupt heat distribution, leading to uneven warmth and increased energy use. Key steps include locating the bleed valves on each baseboard unit, carefully releasing trapped air, and consistently monitoring system pressure to ensure proper operation. Routine maintenance, such as checking for leaks, inspecting the expansion tank, and verifying the automatic air vents, can prevent future air buildup. If problems persist despite these efforts, consulting an HVAC professional for a thorough inspection is highly recommended to safeguard system performance.
About the Author
Adrian Green is a passionate woodworking enthusiast who has dedicated his life to the craft of woodworking. From his early days working alongside his father in the family woodworking shop, Adrian has honed his skills and developed a deep love for creating beautiful, functional pieces with his hands. As the voice behind The Woodenify Blog, he shares his knowledge, tips, and inspiration with fellow woodworkers of all skill levels, helping them build confidence in their abilities while learning new techniques.
Professional Focus
- Specializes in DIY woodworking projects, from furniture making to home décor.
- Provides step-by-step guides, tips, and practical tutorials for woodworkers at any skill level.
- Focused on empowering readers with confidence and knowledge through easy-to-follow instructions and hands-on techniques.
- Passionate about building a community where makers can share, learn, and grow together in the world of woodworking.
Education History
University of Craft and Design – Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) in Woodworking and Furniture Design
Woodworking Apprenticeships – Gained extensive hands-on experience through various workshops and mentorships with seasoned craftsmen, refining carpentry and furniture-making skills.
Expertise
- DIY woodworking, carpentry, furniture making, and home décor projects.
- Creating clear, accessible tutorials and guides for beginner to advanced woodworkers.
- Helping readers experience the satisfaction and fulfillment of turning raw materials into stunning finished products.
